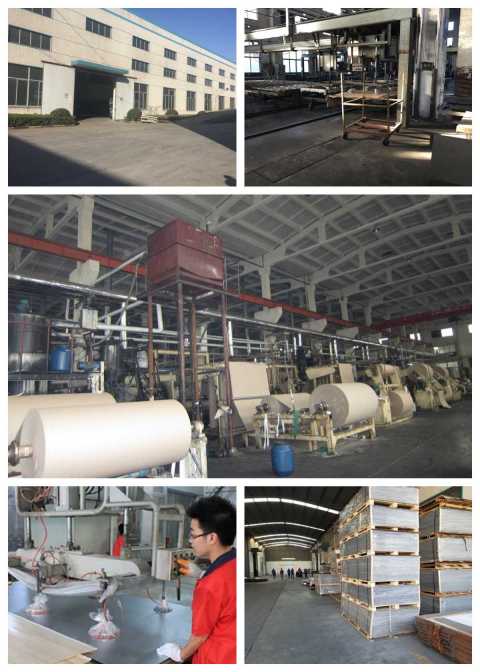
Compact laminate
Compact laminate is a high performance material made by impregnating layers of paper or fabric with thermosetting resins. These saturated layers are then stacked and compressed under high pressure and temperature, forming a dense, solid structure. This process gives HPL superior strength and stability compared to regular laminates.Depending on the base materials and resins used, manufacturers can customize its performance for various applications.

Origins and Early Development
- The development of compact laminate started in the early to mid – 20th century, aiming to meet the demand for durable industrial surfaces.
- As manufacturing technology advanced, improvements in resin formulation and pressing techniques enhanced its chemical resistance and appearance, expanding its use into new industries.
Advancements in Manufacturing
- Today, Compact Laminate production benefits from precise modern processes.
- Advanced machinery enables efficient material impregnation, while computer – controlled presses ensure consistent quality. These improvements have increased production speed and allowed for the creation of thinner yet sturdy products, widening their application scope.

Durability
- Compact laminate excels in durability, withstanding heavy use in high traffic areas.
- In shopping malls, its flooring resists scratches and dents from daily foot and cart traffic.
- In schools, desks and tables made of this material endure rough handling by students.
Chemical Resistance
- It also offers excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for environments with chemical exposure.
- Hospital labs use compact laminate to resist acids, alkalis, and disinfectants, while industrial workshops rely on solid laminate to protect workbenches from chemical spills.
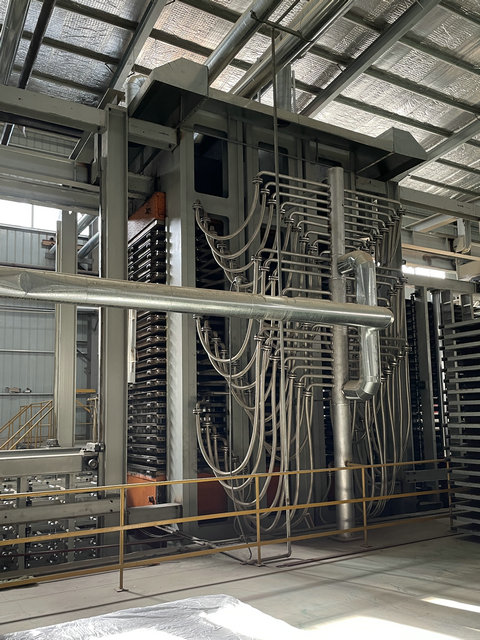

Material Selection
- The production of compact laminate begins with carefully choosing base materials like kraft paper or glass fabric, and thermosetting resins such as phenolic or melamine.
- Quality – controlled sourcing ensures the final product’s reliability.
Impregnation and Lamination
- Selected materials are fully soaked in resin, then precisely stacked and transferred to a hydraulic press.
- High pressure and temperature cure the resin, bonding the layers into a solid sheet of dense laminate.
Quality Control
- Quality control is crucial in HPL production. Manufacturers test for thickness uniformity, strength, and chemical resistance, and inspect for voids or delamination, approving only products that meet strict standards.
Interior Design

- In interior design, compact laminate is popular for countertops, wall cladding, and furniture. In kitchens, it provides a sleek, easy – to – clean, and scratch – resistant surface.
- As wall cladding, it adds texture and color, while furniture made from it combines style and durability.
Architectural Facades
- In architecture, compact laminate creates protective and visually appealing exterior facades. Its durability allows facades to withstand harsh weather, while its dynamic, textured designs can change appearance with sunlight.
Transportation and Public Buildings
- Due to its fire resistant properties, HPL is widely used in transportation and public buildings.
- In high – speed trains, it’s used for interior panels to slow fire spread and reduce toxic fumes.
- Schools and hospitals also use compact for safety and functionality.
Environmental Innovations

- The future of compact laminate focuses on environmental sustainability.
- Manufacturers are developing eco – friendly versions with recycled paper and plant – based resins, and adopting energy – efficient processes to reduce the carbon footprint.
Performance Enhancements
- Ongoing research aims to improve compact laminate performance, such as enhancing heat insulation, soundproofing, stain resistance, and self – cleaning properties, to expand its applications and market competitiveness.

